Client Context
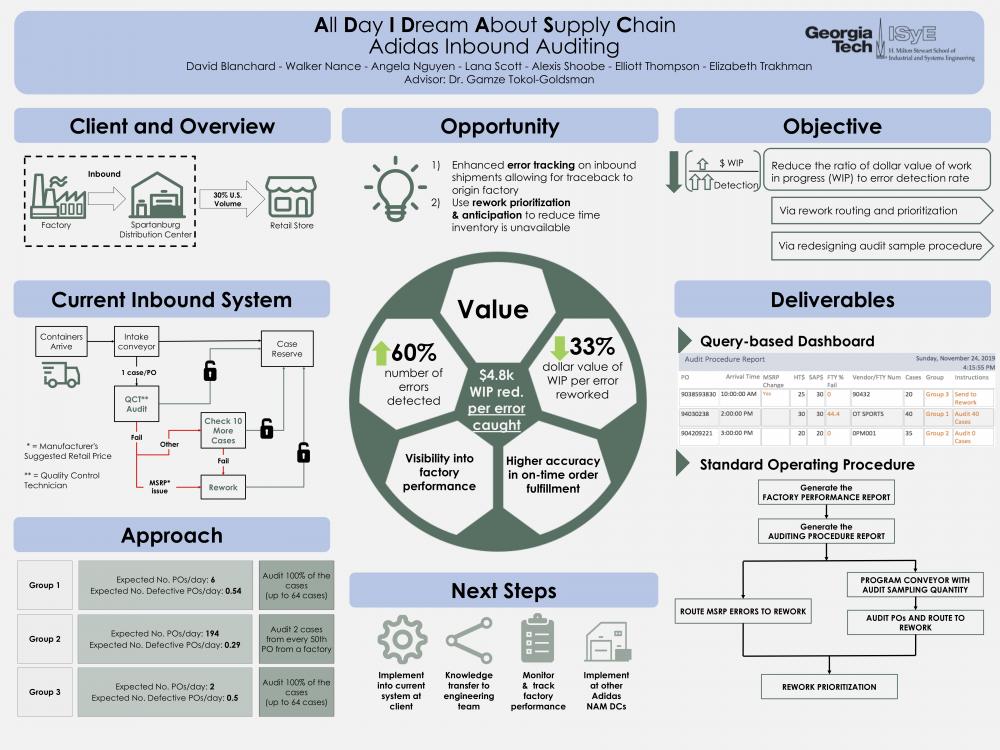
Adidas is a multinational sportswear manufacturer based in Germany with its North American Headquarters located in Portland, Oregon. Its North American distribution network consists of seven distribution center campuses, each with a specified product focus. Adidas North American leadership has detected pain points in its supply chain during the inbound auditing of shipments coming into Adidas distribution centers. Thus, the client has requested an analysis of their current inbound auditing process to identify specific areas of inefficiency that result in delays or errors in their outbound shipments. Our focus in one of the distribution centers at Adidas' Spartanburg, South Carolina campus. This distribution center is currently responsible for 30% of all North American outbound shipments.
Currently, Adidas is running a one-size-fits-all solution for inbound audit processing, in which every inbound purchase order is audited in the same way: one case per purchase order is audited for errors, regardless of the purchase order’s size or its third-party source factory. If a purchase order is flagged for errors during the audit, it is rerouted to a rework process, where the errors are fixed, and all of the items included in the purchase order are virtually “locked”. As a result, purchasers cannot place orders against the inventory until rework is completed.
Project Objective
Our main objective was to reduce the ratio of dollar value of work in progress inventory per error caught in the new system. Work in progress inventory is defined as the price per item in a purchase order multiplied by the quantity of items in that purchase order, and is compounded as POs enter the system, and decreased as they are set to unlocked in the inventory management system. We standardized the value of work in progress in inventory to the number of errors caught, because intrinsically, as more errors are caught, more time is spent in the system due to the rework process, which will increase the work in progress inventory value. By standardizing by errors caught, the tradeoff between time spent ensuring inventory is fit for inventory and the number of errors caught can be managed.
Work in progress inventory value is an important metric because it represents potential lost revenue, as inventory is physically in the system but unable to be ordered by purchasers. Reducing this value shows an improvement in the performance of the inbound auditing process.
Design Strategy
The solution's main goal was to strategically target POs coming from the most problematic factories. The most problematic factories were found by calculating a three standard deviation control chart on factory performance. Corresponding auditing procedures for these factory groupings were evaluated using Bayesian statistics. Simulation was used to validate the approach and ensure feasibility within the system's constraints. This approach was approved by the client as well.
Deliverables
Standard Operating Procedure - the standard operating procedure (SOP), which compiles all recommended changes to the auditing and rework processes into a packet of tasks. Each task contains the following information: a purpose, a time to perform it, how frequently to perform it, and a detailed set of instructions on how to perform it. This will allow all employees involved with any part of the auditing process to easily understand their responsibilities and exactly how to complete them.
Audit Procedure Report - the Microsoft access dashboard that will help Adidas determine the specific audit procedure for each individual PO that comes through the DC. Additionally, it will help keep track of factory performance based on previous error rates of the PO's they have sent.